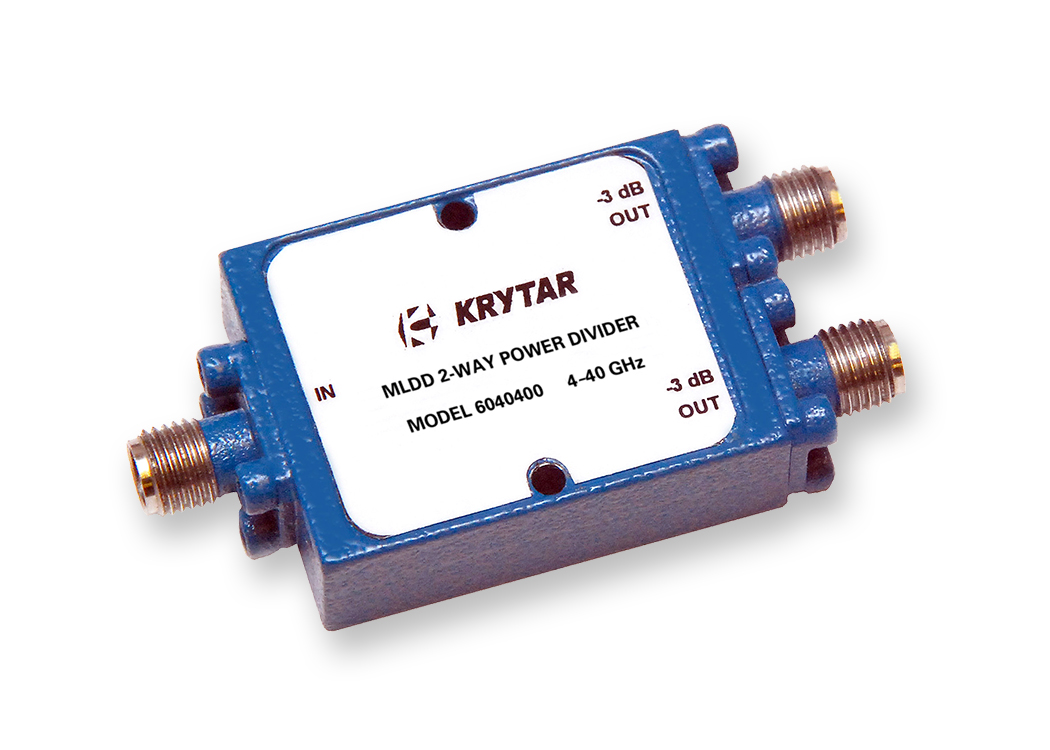
2-Way Power Dividers 6040400
SPECIFICATIONS
Model Number
Freq. Min. (GHz)
Freq. Max. (GHz)
FEATURES
4 – 40 GHz (C thru Ka-Bands) Frequency Operation
Isolation: >14.0 dB
Insertion Loss: <2.1 dB
Amplitude Tracking: ±0.5 dB
2.4-mm Female Connectors
Custom Designs Available
Product Description
KRYTAR MLDD 2-way power dividers lend themselves to emerging wireless ultra-broadband designs and many test and measurement applications. KRYTAR has used its proprietary design to produce a wide assortment of matched-line directional dividers (MLDD) with ultra-high performance over a broadband frequency range. KRYTAR MLDD 2-way power dividers are a new class of patented directional devices.
KRYTAR’s MLDD 2-way power divider, Model 6040400, offers high performance over the ultra-broadband frequency range of 4.0 to 40.0 GHz in a compact, lightweight package.
KRYTAR’s technological advances provide excellent operating performance of this new 2-way unit. Model 6040400 covers the full frequency range from 4.0 to 40.0 GHz with >14.0 dB Isolation and ±0.5 dB of maximum Amplitude Tracking, with maximum Phase Tracking is ±8 degrees. The 2-way divider exhibits Insertion Loss of <2.1 dB across the full frequency range. Maximum Input VSWR is 1.9 and Maximum Output VSWR is 2.1. Input power rating is 10 watts with 2:1 load VSWRs. Units with tighter Amplitude and Phase Tracking specifications can be supplied. Contact the factory with your requirements.
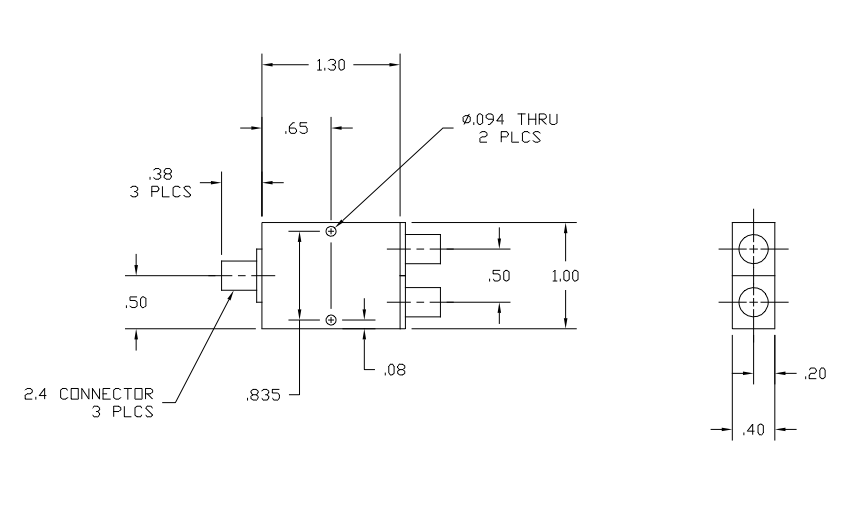
The power divider is a compact package measuring just 1.30 inches (L) x 1.00 inches (W) x 0.40 inches (H), weighs only 1.1-ounces, and comes with standard 2.4-mm coaxial Female Connectors and Optional 2.92-mm Female Connectors.
KRYTAR’s new power divider offers the widest frequency coverage in a single package on the market and provides superior performance. Targeting broadband electronic warfare (EW) systems and complex switch-matrix applications, for example, KRYTAR has used its proprietary design to produce a wide assortment of matched-line directional dividers (MLDD) with ultra-high performance over a broadband frequency range. The directional coupler can also be manufactured to meet ridged military specifications.
KRYTAR also offers complete engineering services for custom designs that meet or exceed critical performance and/or packaging specifications.
Common Definitions
|
Microwave Frequency Bands
|
|
| Band Designation | Frequency Range (GHz) |
| UHF | 300 MHz – 1.0 GHz |
| L | 1.0 – 2.0 |
| S | 2.0 – 4.0 |
| C | 4.0 – 8.0 |
| X | 8.0 – 12.0 |
| DBS | 12.2 – 12.7 |
| Ku | 12.0 – 18.0 |
| K | 18.0 – 26.5 |
| Ka | 26.5 – 40.0 |
| Q | 30.0 – 50.0 |
| U | 40.0 – 60.0 |
| V | 50.0 – 75.0 |
Amplitude and phase tracking are the ratio of one output to the other in dB or degrees respectively.
Power Dividers (also power splitters and, when used in reverse, power combiners) and directional couplers are passive devices. They couple a defined amount of the electromagnetic power in a transmission line to a port enabling the signal to be used in another circuit.
MLDD signifies Matched-line Directional Divider, a new class of microwave directional devices invented and patented by Thomas J. Russell, the founder of KRYTAR.
Directional Couplers: Components that allow two microwave circuits to be combined into one integrated system in one direction with the two completely isolated from each other in the opposite direction.
Couplers are passive microwave components used for distributing or combining microwave signals. Directional couplers are four-port circuits where one port is isolated from the input port.
The coupled port on a microstrip, or stripline directional coupler, is closest to the input port because it is a backward wave coupler. On a waveguide broadwall directional coupler, the coupled port is closest to the output port because it is a forward wave coupler.
Frequency Sensitivity is the amount of frequency change in the carrier frequency per unit amplitude change in the message signal.
Gigahertz (GHz): A unit of measurement denoting the number of cycles in one second. One GHz is one billion cycles every second.
Megahertz (MHz): Equal to 1 million Hz. Uses the SI Prefix Mega, meaning 10^6.
VSWR (Voltage Standing Wave Ratio): The ratio of the maximum voltage to the minimum voltage in standing wave pattern along the length of a transmission line structure. It varies from 1 to (plus) infinity and is always positive. VSWR can be converted to return loss or the reflection coefficient.
Insertion Loss: In telecommunications, Insertion Loss is the loss of signal power resulting from the insertion of a device in a transmission line or optical fiber and is usually expressed in decibels, or dB.
Isolation: In telecommunications, Isolation refers to the ability to prevent a signal from appearing at a node in a circuit where it is unwanted and is expressed in decibels, or dB.
Operating Temperature: An operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the maximum operating temperature (or peak operating temperature). Outside this range of safe operating temperatures the device may fail.
5G
The fifth generation (5G) of cellular service, superseding 4G LTE. Governed by the 3GPP, 5G will increase transmission speed dramatically and embrace prioritization. As wireless data increases exponentially, real-time content such as video calling and video streaming must be given a higher priority than data on Web pages.
5G NR (5G New Radio)
The 5G new radio access technology (RAT) air-interface is a global standard, which like 4G also uses OFDM modulation, and is designed to deliver data rates up to 20 Gbps, enabling individual users to get gigabit-per-second downloads over the air (OTA). Wireless virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) can become commonplace, and 5G is expected to provide a huge boost for connecting billions of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 is the most recent iteration of the IEEE standard for wireless local-area network (WLAN) protocol and is a substantial upgrade over its predecessors Wi-Fi 4 and Wi-Fi 5. Wi-Fi 6 operates between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Wi-Fi 6 can be significantly faster due to technologies like traffic prioritization, OFDMA, and beamforming.
Wi-Fi 6E
Wi-Fi 6E operates at 6 GHz (5.925–7.125 GHz in the U.S.) and also the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz devices already in use. Wi-Fi 6E-enabled devices can take advantage of the newer 6 GHz frequency band for further improved connectivity.
Additional Resources
For more information on Krytar’s Couplers please see below:
- Power Dividers Primer
- Microwave or RF Amplifier Test Setup
- Krytar Directional Couplers: Term Definitions, Testing, and Typical Applications
- 180-Deg. Hybrids Control Signals From 2 to 20 GHz, Microwaves & RF article
- Broadband, 3dB 90° Hybrids Cover 1 to 18 GHz, Microwave Journal article
- Krytar 180 Degree Hybrids Control Signals from 1 to 26.5 GHz
- Krytar 180 Degree Hybrids testing and term definition